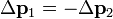The concept of coupling and exchange of angular momentum seems to be wrong
Version: 05.01.2010
Discussion:
But atmosphere physicists and others believed so far, that this is possible.
There exists no Newtons law, which describes the exchange of angular momentum.
The exchange of momentum is the result of the law actio = reactio.
But angular momentum is in the sense of Newtons mechanic no momentum: the result of a force, which is applied over a time.
Therfore angular momentum can't be exchanged - but physicists believed in this theory so far.
For example:
' Exchange of Atmospheric Angular Momentum between the Hemispheres '
IN regions of surface easterly winds (where the surface is moving in space faster than the air) a transfer of westerly relative angular momentum
takes place from the Earth's surface to the atmosphere, while in regions of surface westerlies the transfer is from the atmosphere to Earth.
These transfers are necessarily accompanied by transports of angular momentum within the atmosphere from low latitudes, where
easterly winds prevail, to middle latitudes where westerly winds prevail.
http://www.nature.com/nature/journal/v221/n5178/abs/221352b0.html
Therfore a coupling of angular momentums doesn`t exist.
But a coupling is assumed in Quantum mechanics.
Two rotating systems only interact over exchange of momentum, like Newtons laws discribes.
- but not over exchange of angular momentum.
But its paradox: Physcists assumed so far, that Newtons law could be applicable to the
concept of a designed angular momentum, too.
But the momentum is the result of a force, not the angular momentum.
This is mathematically impossible, too.
The force could be the force, which couples two rotating systems.
The 'real' angular momentum is only the momentum part 'p' of the designed
angular momentum.
http://de.wikipedia.org/wiki/Drehimpuls
Thus 'p' with 'v' :
But it seems so as if they never have imagined, hat its only possible that systems exchange real momentum in the senses of Newton.
But this transferred momentum has really nothing to do with the radius 'r' of a rotating system.
But the kinetically rotationally energy has to do with the radius 'r'.
But you can asign a angular momentum to the new coupled system.
But this angular momentum has nothing to do with the vektor sum of angular momentums.
This vektor sum doesn't correspond to the rotationally energy.
A vektor sum of designed angular momentums is not possible - it doesn`t fit to the rotationally energy
of the coupled rotationally systems..
This is conserved.
A catastrophe for physics.
Nothing else is imaginable.
But you can find a exchange of rotationally energy by exchange of momentum in Newtons sense.
Its not possible, to imagine an angular momentum as momentum.
Its better to construct a vector with the amount of the rotationally energy if one wants to describe
the exchange of kinetically energy of rotating systems.
---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Momentum#Conservation_of_linear_momentum
In an isolated system (one where external forces are absent) the total momentum will be constant: this is implied by Newton's first law of motion. Newton's third law of motion, the law of reciprocal actions, which dictates that the forces acting between systems are equal in magnitude, but opposite in sign, is due to the conservation of momentum.
Since position in space is a vector quantity, momentum (being the canonical conjugate of position) is a vector quantity as well—it has direction. Thus, when a gun is fired, the final total momentum of the system (the gun and the bullet) is the vector sum of the momenta of these two objects. Assuming that the gun and bullet were at rest prior to firing (meaning the initial momentum of the system was zero), the final total momentum must also equal 0.
In an isolated system with only two objects, the change in momentum of one object must be equal and opposite to the change in momentum of the other object. Mathematically,
Momentum has the special property that, in a closed system, it is always conserved, even in collisions and separations caused by explosive forces. Kinetic energy, on the other hand, is not conserved in collisions if they are inelastic. Since momentum is conserved it can be used to calculate an unknown velocity following a collision or a separation if all the other masses and velocities are known.
A common problem in physics that requires the use of this fact is the collision of two particles. Since momentum is always conserved, the sum of the momenta before the collision must equal the sum of the momenta after the collision:
where u1 and u2 are the velocities before collision, and v1 and v2 are the velocities after collision.
Der Drehimpuls ist ein konstante Größe bei Bewegungen von Massen in Zentralfeldern.
http://sites.google.com/site/steppatscience/home/drehi
Der Begriff Drehimpuls ist irreführend:
Es handelt sich bei dieser Erhaltungsgröße in Zentralkraftfeldern nicht um einen Impuls.
Der Drehimpuls  eines Massenpunktes ist das Kreuzprodukt seines Ortsvektors
eines Massenpunktes ist das Kreuzprodukt seines Ortsvektors 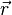 mit seinem Impuls
mit seinem Impuls 
P = m times v
IN regions of surface easterly winds (where the surface is moving in space faster than the air) a transfer of westerly relative angular momentum
takes place from the Earth's surface to the atmosphere, while in regions of surface westerlies the transfer is from the atmosphere to Earth.
These transfers are necessarily accompanied by transports of angular momentum within the atmosphere from low latitudes, where
easterly winds prevail, to middle latitudes where westerly winds prevail.
http://www.nature.com/nature/journal/v221/n5178/abs/221352b0.html
----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
But there exists no exchange of angular momentums because there exists no kind of angular momentum in the sense of a momentum.
- But there exsts no transfer of angular momentum. This kind of thinking is impossible.
- The physical vector angular momentum has been misunderstood so far.
The exchange of angular momentum, which is no real momentum, is fiction in atmosphere physics.
There exists no Newtons law, wich describes the possibility of exchange and coupling of angular momentum.
A coupling of angular momentum is not possible. This is a very new aspect in physics.
A coupling of angular momentum doesn't correspond with the law of conservation of rotational energy.
Therefore the concept of angular momentum is generally misused in modern physics.
One can show this in easy constallations.
Investigate the coupling of two rotating rigid systems:

The vektors L (1) and L (2) have for example the same or opposite direction.
Its too easy to show, that the rotational energy of the whole system doesn`t correspond to the angular momentum of the whole system, if this angular momentum is evaluated as sum of angular momentums.
Both equations are not compatible.
QM- theory with the model of coupling of angular momentum and atmosphere physics seem to be wrong.
The theoretical atmosphere physics is based on the concept of exchange
of angular momentum.